Ops … I did it again – MLOps with Kubeflow, MLflow
24 Oct 2020
Machine Learning is one of the hottest area nowadays. New algorithms and models are widely used in commercial solutions thus the whole ML process as a software development and deployment process needs to be optimized.
Kubeflow is an opensource platform which allows to build complete multi-user analytical environment. It is setup on the Kubernetes thus it can be simply installed on a public cloud, on premise Kubernetes cluster or on your workstation.
On the other hand MLFlow is a platform which can be run as standalone application. It doesn’t require Kubernetes thus the setup much more simpler then Kubeflow but it doesn’t support multi-user/multi-team separation.
In this article we will use Kubeflow and MLflow to build the isolated workspace and MLOps pipelines for analytical teams.
Currently we use Kubeflow platform in @BankMillennium to build AI solutions and conduct MLOPS process and this article is inspired by the experience gained while launching and using the platform.
Before you will continue reading please watch short introduction:
AI Platform
The core of the platform will be setup using Kubeflow (version 1.0.1) on Kubernetes (v1.17.0). The Kuberenetes was setup using Rancher RKE which simplifies the installation.
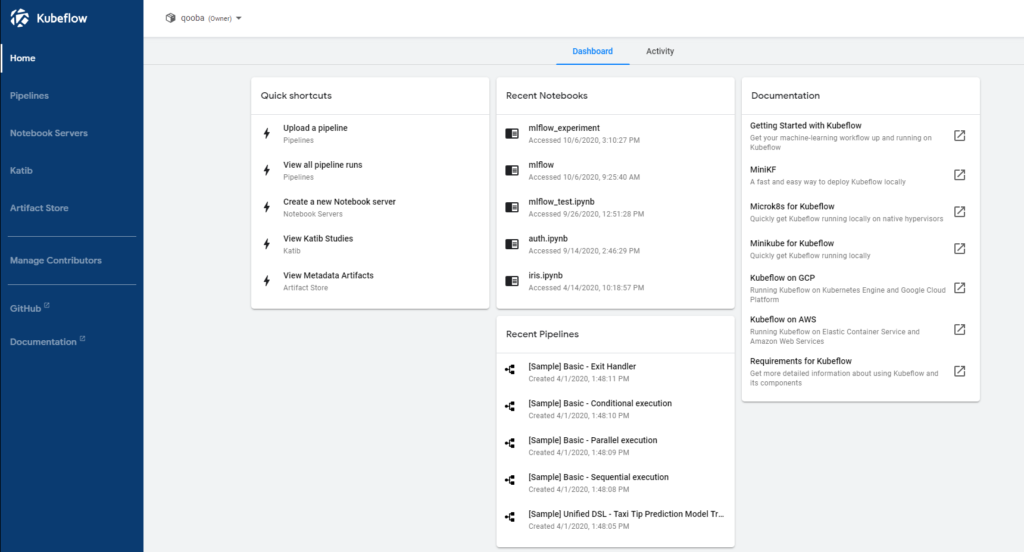
The Kubeflow gives complete analytical multi-user/multi-teams environment with: authentication (dex), jupyter notebook workspace, pipelines, metadata store, artifact store, models deployment engines (kfserving, seldon).
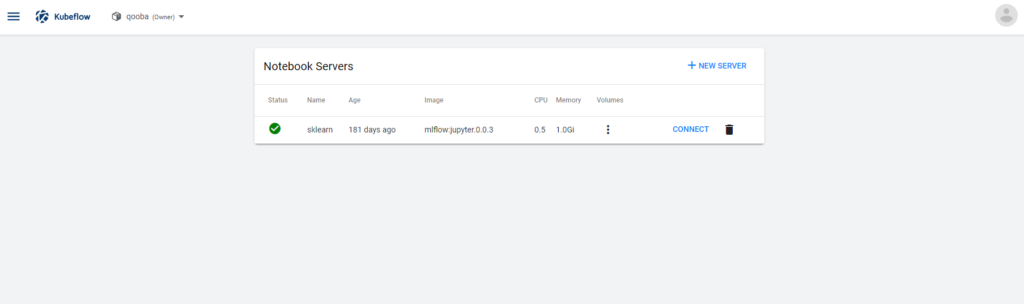
Namespace isolation
The user namespaces by default are isolated in Kubeflow UI but in fact are not isolated at all.
The ServiceRoleBinding configuration is very naive and checks only kubeflow-userid header to check RBAC access.
apiVersion: rbac.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: ServiceRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
role: admin
user: admin@kubeflow.org
namespace: qooba
ownerReferences:
- apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1
blockOwnerDeletion: true
controller: true
kind: Profile
name: qooba
uid: 400b5e7b-4b58-40e7-8613-7b0ef01a55ba
spec:
roleRef:
kind: ServiceRole
name: ns-access-istio
subjects:
- properties:
request.headers[kubeflow-userid]: admin@kubeflow.org
Thus we can simply access other namespace notebook from notebooks in different namespace setting kubeflow-userid header:
import requests
url='http://..svc.cluster.local'
headers={
'kubeflow-userid': "admin@kubeflow.org"
}
requests.get(url,headers=headers).text
To fix this we can setup appropriate Kubernetes NetworkPolicies eg.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-ingress-default
namespace:
spec:
podSelector: {}
ingress:
- from:
- namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- {key: namespace, operator: In, values: [, kubeflow, istio-system, kube-system]}
policyTypes:
- Ingress
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: deny-egress-all
namespace:
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-egress-dns
namespace:
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
namespace: kube-system
ports:
- protocol: UDP
port: 53
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-egress-istio
namespace:
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
namespace: istio-system
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-egress-kubeflow
namespace:
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
namespace: kubeflow
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: allow-egress-internal
namespace:
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels: {}
policyTypes:
- Egress
egress:
- to:
- namespaceSelector:
matchLabels:
namespace:
Isolated model registry
By default Kubeflow is equipped with metadata and artifact store shared between namespaces which makes it difficult to secure and organize spaces for teams. To fix this we will setup separate MLflow Tracking Server and Model Registry for each team namespace.
MLflow docker image qooba/mlflow:
FROM continuumio/miniconda3
RUN apt update && apt install python3-mysqldb default-libmysqlclient-dev -yq
RUN pip install mlflow sklearn jupyterlab watchdog[watchmedo] boto3
RUN conda install pymysql
ENV NB_PREFIX /
CMD ["sh","-c", "jupyter notebook --notebook-dir=/home/jovyan --ip=0.0.0.0 --no-browser --allow-root --port=8888 --NotebookApp.token='' --NotebookApp.password='' --NotebookApp.allow_origin='*' --NotebookApp.base_url=${NB_PREFIX}"]
mlflow.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mlflow-pv-claim
namespace: qooba
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage
volumeMode: Filesystem
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: mlflow
namespace: qooba
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mlflow
namespace: qooba
labels:
app: mlflow
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: mlflow
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mlflow
namespace: qooba
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mlflow
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mlflow
version: v1
spec:
serviceAccountName: mlflow
containers:
- image: qooba/mlflow
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mlflow
command: ["mlflow","server","-h","0.0.0.0","--backend-store-uri","sqlite:///mlflow/mlflow.db","--default-artifact-root","s3://mlflow/mlruns"]]
#command: ["mlflow","server","-h","0.0.0.0","--backend-store-uri","mysql+pymysql:///mlflow/mlflow.db","--default-artifact-root","s3://mlflow/mlruns"]]
#command: ["mlflow","server","-h","0.0.0.0","--backend-store-uri","sqlite:///mlflow/mlflow.db","--default-artifact-root","/mlflow/mlruns"]]
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: minio
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: minio123
- name: MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL
value: http://minio.qooba.svc.cluster.local:9000
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mlflow
name: mlflow
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
volumes:
- name: mlflow
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mlflow-pv-claim
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
name: dshm
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: mlflow
namespace: qooba
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- qooba/mlflow-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /
rewrite:
uri: /
route:
- destination:
port:
number: 5000
host: mlflow
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: mlflow-gateway
namespace: qooba
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- '*'
port:
name: http
number: 5000
protocol: HTTP
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: mlflow-filter
namespace: istio-system
spec:
filters:
- filterConfig:
httpService:
authorizationRequest:
allowedHeaders:
patterns:
- exact: cookie
- exact: X-Auth-Token
authorizationResponse:
allowedUpstreamHeaders:
patterns:
- exact: kubeflow-userid
serverUri:
cluster: outbound|8080||authservice.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
failureModeAllow: false
timeout: 10s
uri: http://authservice.istio-system.svc.cluster.local
statusOnError:
code: GatewayTimeout
filterName: envoy.ext_authz
filterType: HTTP
insertPosition:
index: FIRST
listenerMatch:
listenerProtocol: HTTP
listenerType: GATEWAY
portNumber: 5000
workloadLabels:
istio: ingressgateway
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: dex-mlflow
namespace: auth
spec:
gateways:
- qooba/mlflow-gateway
hosts:
- '*'
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /dex/
route:
- destination:
host: dex.auth.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 5556
additionally we have to edit istio gateway and add mlflow to access the mlflow UI:
kubectl edit svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
and add:
spec:
ports:
...
- name: mlflow
nodePort: 31382
port: 5000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 5000
The MLflow repository can be accessed from web browser:
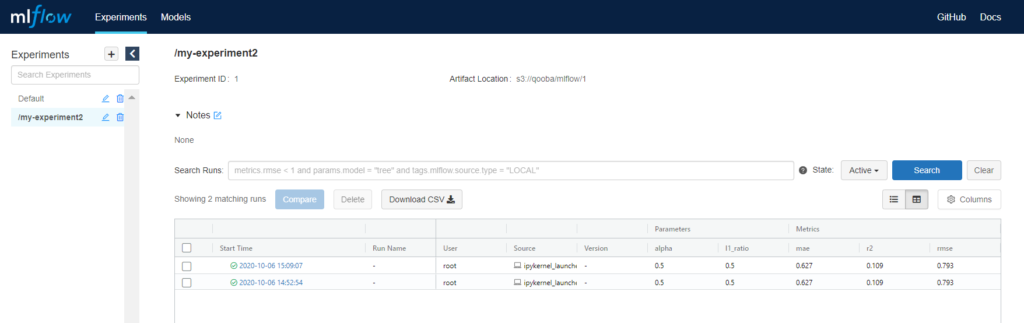
Additionally we have to mount PersistentVolume mlflow-pv-claim to user notebook where we will store the training artifacts:
kubectl edit Notebook -n qooba sklearn
apiVersion: kubeflow.org/v1
kind: Notebook
metadata:
labels:
app: sklearn
name: sklearn
namespace: qooba
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- env: []
image: qooba/mlflow
name: sklearn
resources:
requests:
cpu: "0.5"
memory: 1.0Gi
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/jovyan
name: workspace-sklearn
- mountPath: /mlflow
name: mlflow
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
serviceAccountName: default-editor
ttlSecondsAfterFinished: 300
volumes:
- name: workspace-sklearn
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: workspace-sklearn
- name: mlflow
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mlflow-pv-claim
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
name: dshm
Now analysts can log models and metrics from jupyter notebook workspace (code example from https://www.mlflow.org/docs/latest/tutorials-and-examples/tutorial.html):
import os
import warnings
import sys
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import ElasticNet
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import mlflow
import mlflow.sklearn
import logging
remote_server_uri='http://mlflow:5000'
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(remote_server_uri)
mlflow.set_experiment("/my-experiment2")
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARN)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
def eval_metrics(actual, pred):
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(actual, pred))
mae = mean_absolute_error(actual, pred)
r2 = r2_score(actual, pred)
return rmse, mae, r2
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
np.random.seed(40)
# Read the wine-quality csv file from the URL
csv_url = (
"./winequality-red.csv"
)
try:
data = pd.read_csv(csv_url, sep=";")
except Exception as e:
logger.exception(
"Unable to download training & test CSV, check your internet connection. Error: %s", e
)
train, test = train_test_split(data)
train_x = train.drop(["quality"], axis=1)
test_x = test.drop(["quality"], axis=1)
train_y = train[["quality"]]
test_y = test[["quality"]]
alpha = 0.5
l1_ratio = 0.5
with mlflow.start_run():
lr = ElasticNet(alpha=alpha, l1_ratio=l1_ratio, random_state=42)
lr.fit(train_x, train_y)
predicted_qualities = lr.predict(test_x)
(rmse, mae, r2) = eval_metrics(test_y, predicted_qualities)
print("Elasticnet model (alpha=%f, l1_ratio=%f):" % (alpha, l1_ratio))
print(" RMSE: %s" % rmse)
print(" MAE: %s" % mae)
print(" R2: %s" % r2)
mlflow.log_param("alpha", alpha)
mlflow.log_param("l1_ratio", l1_ratio)
mlflow.log_metric("rmse", rmse)
mlflow.log_metric("r2", r2)
mlflow.log_metric("mae", mae)
tracking_url_type_store = urlparse(mlflow.get_tracking_uri()).scheme
if tracking_url_type_store != "file":
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(lr, "model", registered_model_name="ElasticnetWineModel2")
else:
mlflow.sklearn.log_model(lr, "model")
I definitely recommend to use git versioned MLflow projects instead of running code directly from jupyter because MLflow model registry will keep the git commit hash used for the run which will help to reproduce the results.
MLOps
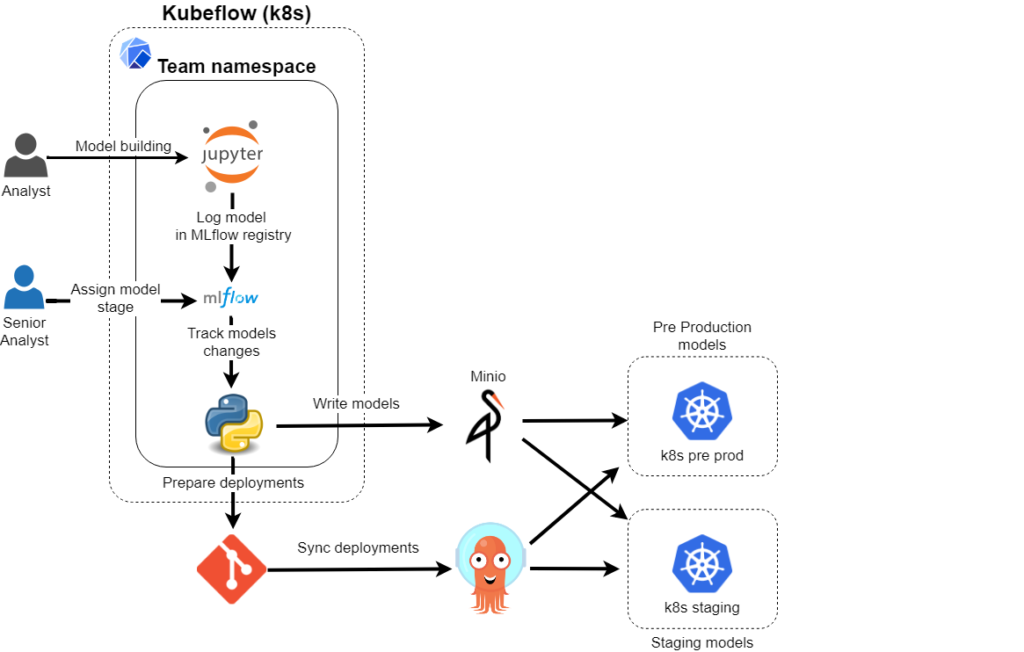
Now I’d like to propose the process of building and deploying ML models.
Training
As described before the model is prepared and trained by the analyst which works in the Jupyter workspace and logs metrics and model to the MLflow tracking and model registry.
MLflow UI
Senior Analyst (currently the MLflow doesn’t support roles assignment) checks the model metrics and decides to promote it to Staging/Production stage in MLflow UI.
Model promotion
We will create additional application which will track the changes in the MLflow registry and initialize the deployment process.
The on each MLflow registry change the python application will check the database, prepare and commit k8s deployments and upload models artifacts to minio.
Because the applications commits the deployments to git repository we need to generate ssh keys:
ssh-keygen
and store them as a secrets:
kubectl create secret generic ssh-key-secret --from-file=id_rsa=./id_rsa --from-file=id_rsa.pub=./id_rsa.pub -n qooba
Now we can deploy the application:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mlflowwatch
namespace: qooba
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mlflowwatch
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mlflowwatch
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: qooba/mlflow:watchdog
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mlflowwatch
command: ["/mlflow/start-watch.sh"]
env:
- name: GIT_REPO_URL
value: ...
- name: GIT_REPO_IP
value: ...
- name: BUCKET_NAME
value: qooba
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: minio
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: minio123
- name: MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL
value: http://minio.qooba.svc.cluster.local:9000
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /mlflow
name: mlflow
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
- mountPath: /etc/ssh-key
name: ssh-key-secret-volume
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: mlflow
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mlflow
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
name: dshm
- name: ssh-key-secret-volume
secret:
defaultMode: 256
secretName: ssh-key-secret
start-watch.sh:
#!/bin/bash
watchmedo shell-command --patterns='*.db' --recursive --wait --command='/mlflow/watch.sh' /mlflow
watch.sh
#!/bin/bash
cd /mlflow
if [ ! -d "/root/.ssh" ]
then
cp -r /etc/ssh-key /root/.ssh
chmod -R 700 /root/.ssh
ssh-keygen -R $GIT_REPO_URL
ssh-keygen -R $GIT_REPO_IP
ssh-keygen -R $GIT_REPO_URL,$GIT_REPO_IP
ssh-keyscan -H $GIT_REPO_URL,$GIT_REPO_IP >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H $GIT_REPO_IP >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
ssh-keyscan -H $GIT_REPO_URL >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
git config --global user.name "mlflowwatch"
git config --global user.email "mlflowwatch@qooba.net"
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/master master
fi
python3 /mlflow/watch.py
git add .
git commit -a -m "mlflow autocommit"
git push origin master
watch.py:
import os
import jinja2
import sqlite3
from collections import defaultdict
import boto3
import botocore
class Watcher:
def __init__(self):
self._model_deployment=ModelDeployment()
self._model_registry=ModelRegistry()
self._model_store=ModelStore()
def process(self):
model_groups = self._model_registry.models_info()
for model_name, models_data in model_groups.items():
print(f'{model_name}:')
for model_data in models_data:
print(f"- stage: {model_data['stage']}")
print(f" path: {model_data['path']}")
self._model_deployment.generate_deployment(model_name, model_data)
self._model_store.upload_model(model_data)
class ModelDeployment:
def __init__(self):
self._create_dir('deployments')
self._template=self._prepare_template()
def generate_deployment(self, model_name, model_data):
self._create_dir(f'deployments/{model_name}')
stage = model_data['stage'].lower()
path = model_data['path'].replace('/mlflow/mlruns','s3://qooba/mlflow')
self._create_dir(f'deployments/{model_name}/{stage}')
outputText = self._template.render(model=path)
with open(f'deployments/{model_name}/{stage}/deployment.yaml','w') as f:
f.write(outputText)
def _create_dir(self, directory):
if not os.path.exists(directory):
os.makedirs(directory)
def _prepare_template(self):
templateLoader = jinja2.FileSystemLoader(searchpath="./")
templateEnv = jinja2.Environment(loader=templateLoader)
return templateEnv.get_template("deployment.yaml")
class ModelRegistry:
def __init__(self):
self._conn = sqlite3.connect('/mlflow/mlflow.db')
def models_info(self):
models=self._conn.execute("SELECT distinct name, version, current_stage, source FROM model_versions where current_stage in ('Staging','Production') order by version desc;").fetchall()
res=defaultdict(list)
for s in models:
res[s[0].lower()].append({"tag": str(s[1]), "stage": s[2], "path": s[3]})
return dict(res)
class ModelStore:
def __init__(self):
self._bucket_name=os.environ['BUCKET_NAME']
self._s3=self._create_s3_client()
self._create_bucket(self._bucket_name)
def upload_model(self, model_data):
path = model_data['path']
s3_path = path.replace('/mlflow/mlruns','mlflow')
try:
self._s3.head_object(Bucket=self._bucket_name, Key=f'{s3_path}/MLmodel')
except botocore.errorfactory.ClientError as e:
files = [(f'{path}/{f}',f'{s3_path}/{f}') for f in os.listdir(path) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(path, f))]
for file in files:
self._s3.upload_file(file[0], self._bucket_name, file[1])
def _create_s3_client(self):
return boto3.client('s3',
aws_access_key_id=os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"],
aws_secret_access_key=os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"],
endpoint_url=os.environ["MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL"])
def _create_bucket(self, bucket_name):
try:
self._s3.head_bucket(Bucket=bucket_name)
except botocore.client.ClientError as e:
self._s3.create_bucket(Bucket=bucket_name)
if __name__ == "__main__":
Watcher().process()
The model deployments will be prepared using the template: deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mlflow-t1
namespace: qooba
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mlflow-t1
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mlflow-t1
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: qooba/mlflow:serving
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mlflow-t1
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: minio
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: minio123
- name: MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL
value: http://minio.qooba.svc.cluster.local:9000
- name: MODEL
value:
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
volumes:
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
name: dshm
If the model is promoted to the Staging/Production the process prepares the deployment yaml and uploads model to S3 store.
We will use minio as a S3 model store.
minio.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: minio
namespace: qooba
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: minio-pv-claim
namespace: qooba
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 10Gi
storageClassName: managed-nfs-storage
volumeMode: Filesystem
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: minio
namespace: qooba
name: minio
namespace: qooba
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app: minio
namespace: qooba
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: minio
namespace: qooba
spec:
serviceAccountName: minio
containers:
- args:
- server
- /data
env:
- name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY
value: minio
- name: MINIO_SECRET_KEY
value: minio123
image: minio/minio:RELEASE.2018-02-09T22-40-05Z
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: minio
ports:
- containerPort: 9000
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: data
subPath: minio
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: minio-pv-claim
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: minio
namespace: qooba
name: minio
namespace: qooba
spec:
ports:
- port: 9000
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9000
selector:
app: minio
namespace: qooba
ArgoCD
No it is time to setup ArgoCD which will sync the Git deployments changes with Kubernetes configuration and automatically deploy newly promoted models.
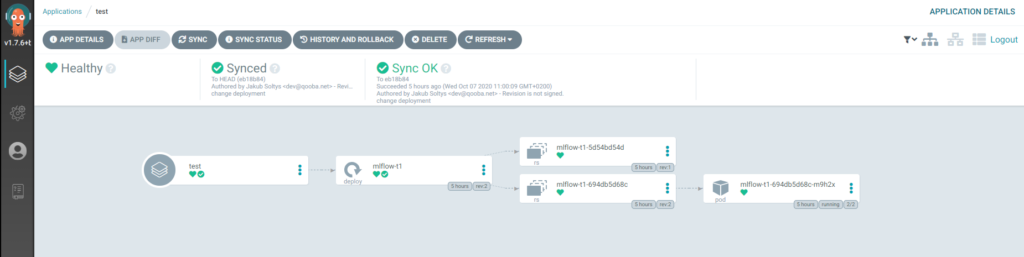
To deploy MLflow models we will use docker image
qooba/mlflow:serving
FROM continuumio/miniconda3
RUN pip install mlflow==1.11.0 cloudpickle==1.6.0 scikit-learn==0.23.2 gevent boto3
ENV GUNICORN_CMD_ARGS="--timeout 60 -k gevent"
WORKDIR /opt/mlflow
ENV PORT=5000
ENV WORKER_NUMBER=4
CMD mlflow models serve -m $MODEL -h 0.0.0.0 -p $PORT -w $WORKER_NUMBER --no-conda
and configuration: mlflow.serving.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: mlflow-t1
namespace: qooba
labels:
app: mlflow-t1
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: mlflow-t1
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mlflow-t1
namespace: qooba
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mlflow-t1
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mlflow-t1
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- image: qooba/mlflow:serving
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: mlflow-t1
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: minio
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: minio123
- name: MLFLOW_S3_ENDPOINT_URL
value: http://minio.qooba.svc.cluster.local:9000
- name: MODEL
value: s3://qooba/mlflow/1/e0167f65abf4429b8c58f56b547fe514/artifacts/model
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /dev/shm
name: dshm
volumes:
- emptyDir:
medium: Memory
name: dshm
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: mlflow-t1
namespace: qooba
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- qooba/mlflow-serving-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /serving/qooba/t1
rewrite:
uri: /
route:
- destination:
port:
number: 5000
host: mlflow-t1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: mlflow-serving-gateway
namespace: qooba
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- '*'
port:
name: http
number: 5000
protocol: HTTP
Each time new model is promoted the ArgoCD applies new deployment with the new model s3 path:
- name: MODEL
value: s3://qooba/mlflow/1/e0167f65abf4429b8c58f56b547fe514/artifacts/model
Inference services
Finally we can access model externally and generate predictions. Please note that in article the model is deployed in the same k8s namespace (in real solution model will be deployed on the separate k8s cluster) thus to access the model I have to send authservice_session otherwise request will redirected to the dex login page.
import json
import requests
import getpass
authservice_session = getpass.getpass()
headers={
'Cookie': f'authservice_session={authservice_session}',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
data={
"columns": ["fixed acidity","volatile acidity","citric acid","residual sugar","chlorides","free sulfur dioxide","total sulfur dioxide","density","pH","sulphates","alcohol"],
"data": [[7.4,0.7,0,1.9,0.076,11,34,0.9978,3.51,0.56,9.4],
[7.8,0.88,0,2.6,0.098,25,67,0.9968,3.2,0.68,9.8]]
}
url='http://qooba-ai:31382/serving/qooba/t1/invocations'
requests.post(url, headers=headers,data=json.dumps(data)).text
# Response: [5.576883967129615, 5.50664776916154]